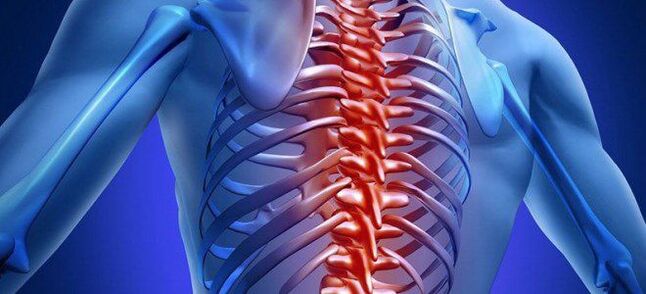
Osteochondrosis of the chest - causes
- Connection and retention of adjacent vertebral bodies;
- Spinal shock-absorbing protection to prevent injuries due to gravity and load;
- Ensure mobility of adjacent vertebrae relative to each other.
- Systemic metabolic disorders in the body;
- being overweight;
- Malnutrition, drinking habits;
- Inactive;
- Sedentary work;
- bad posture;
- flatfoot;
- Back and spine injuries;
- Strenuous physical labor or sports training;
- Pregnant;
- Wear uncomfortable shoes, high heels.
Degree of thoracic osteochondrosis
Grade 1 thoracic osteochondrosis
Thoracic osteochondrosis grade 2

Thoracic osteochondrosis grade III
Thoracic osteochondrosis grade 4
Thoracic Osteochondrosis - Symptoms
- back and chest pain;
- A squeezing sensation in the chest;
- Tingling in the extremities;
- Numbness in arms, legs, neck, shoulders;
- Stiffness and pain in the back and limbs;
- Upper and mid-back muscle spasms;
- There is limited movement of the spine in this area (difficulty bending the body).
Pain caused by thoracic osteochondrosis
- raise your hands;
- Neck rotation;
- moving heavy objects;
- sudden movements;
- Increase physical activity;
- Difficulty breathing, coughing, sneezing;
- Low temperature.
Will thoracic osteochondrosis cause shortness of breath?
- Headache, dizziness;
- Pain in the heart area;
- Breast soreness;
- Rib pain (similar in appearance to pancreatitis or cholecystitis);
- Upper abdominal pain not related to eating;
- Pharyngeal and esophageal discomfort, foreign body sensation;
- Sexual dysfunction.

Thoracic osteochondrosis syndrome
- back pain;
- back.
Thoracic back pain
dorsal thoracic spine
- sharp, dagger-like pain;
- Pain in the area between the ribs and between the shoulder blades;
- Typically, an attack occurs after staying in a position for an extended period of time;
- Pain worsened when rotating torso;
- Difficulty breathing and severe muscle tension.
Thoracic Osteochondrosis - Consequences
- vegetative vascular dystonia;
- Migraine;
- Damage to the function of internal organs (liver, kidney, etc. );
- Hearing and vision loss;
- Epicondylitis of the elbow joint;
- Paresis and paralysis of the arms;
- Axial inflorescence;
- Loss of sensitivity of skin tissue;
- Disability, etc.

How is thoracic osteochondrosis treated?
- Muscle relaxants;
- Chondroprotectant;
- Corticosteroids, etc.
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- manual therapy;
- spinal traction;
- Physical therapy procedures (laser, ultrasound, etc. ).