Osteochondrosis is a concept used to represent a group of diseases related to degenerative and dystrophic changes in the structure of the spine. First, the intervertebral discs are affected, and as the disease progresses, the vertebrae themselves will also be affected. Degeneration is a change associated with the process of tissue wear, aging, loss of original properties, and malnutrition-changes caused by tissue dystrophy. Therefore, the term osteochondrosis connects most non-inflammatory spinal pathologies.
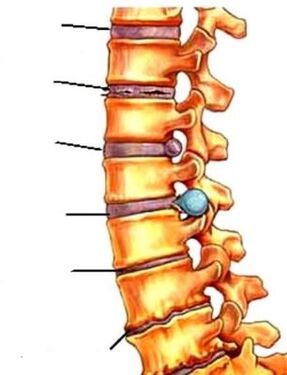
The spine forms the backbone of the bones and connects the various parts of the skeletal system. It supports the head, ribs and muscles. The spinal cord passes through the spine, and the brain is connected to all parts of our body through the spine. Human is the only biped animal in the world, and the spine is designed to provide bipedal movement. Therefore, the spine has a curved shape, reminiscent of the letter S in the Latin alphabet. It is not a rigid rod, but a complex structure made up of fixed elements-vertebrae. This structure of the spine allows us to perform various sports, become flexible and absorb shocks and vibrations. The function of the shock absorber is performed by the intervertebral disc-the cartilage layer composed of the nucleus pulposus and the fibrous annulus surrounding it. The nucleus bears and absorbs the load, and the fibrous ring prevents the nucleus from flattening under pressure.
Decreased disc elasticity may be the beginning of a series of problems. Unable to bear the load, the intervertebral discs begin to deform, and the spine loses its correct shape. The development of the disease leads to further destruction of the intervertebral disc, rupture of the fibrous annulus, and hard contact between the vertebrae, which may pinch the nerves connecting the spinal cord and various parts of the body. This is how osteochondrosis develops. Intervertebral hernias occur, and inflammation often occurs. Without shock absorption, the vertebrae will flatten, and their joints will form scars and bone growth together.
Osteochondrosis is one of the most common diseases. Only cardiovascular disease is more common. It is estimated that every second of the inhabitants of the earth suffer from osteochondrosis. Osteochondrosis is more common in women, but in men, its manifestations are more painful on average.
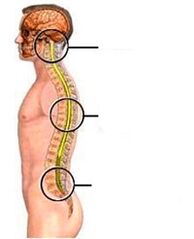
What is osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis affects all parts of the spine. According to the departments most affected by the disaster, there are:
- Lumbar osteochondrosis-occurs most often;
- Cervix-ranked second in "popularity";
- Sacrum
- chest;
- Widespread osteochondrosis, in which several parts of the spine are affected at the same time;
- Cross pathology (lumbosacral or cervical thoracic).
Causes of osteochondrosis
There are many causes of osteochondrosis.
First, as we age, the elasticity of the intervertebral disc is gradually lost. This means that our back needs special attention. Staying in a position that causes the spine to tilt for a long time can cause irreversible changes. You should avoid sitting in an asymmetrical posture, get rid of the habit of lying on one side, and use only one hand to carry heavy objects (such as bags).
A sedentary lifestyle has an adverse effect on spine health. Exercise is necessary, but physical activity should be moderate. The spine should have a chance to recover from the load, and it is also advisable to avoid injury that will also lead to spinal disease.
The second group of causes is related to metabolic disorders and malnutrition. Foods rich in carbohydrates and fats fill the body with calories, and in sedentary urban life, we often have nowhere to go; as a result, energy is deposited in the form of fatty tissue, creating excess weight. Obesity will increase the load on the spine, leading to the development of osteochondrosis. In addition, this diet usually contains insufficient amounts of trace elements (calcium, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, manganese, etc. ), and these elements are essential for strengthening bone tissue. Being overweight is usually caused by endocrine diseases. At the same time, energy, water, or mineral metabolism disorders can also negatively affect the tissues involved in the spinal structure.
The factors leading to the development of osteochondrosis can be:
- flatfoot;
- Hormonal changes;
- Infectious diseases;
- Local circulatory disorders,
And some other factors.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
In the initial stage of osteochondrosis, there are no obvious symptoms. The development of osteochondrosis can be assumed under the following conditions:
- Dull back pain (in the affected area of the spine);
- The back feels heavy and the spine muscles continue to tense;
- Muscle numbness and "goose bumps" appear. In this case, it is usually said "back numbness";
- Tighten when turning the body and neck;
- Headache, dizziness, tinnitus (usually accompanied by cervical osteochondrosis);
- Chest pain (usually accompanied by sternal osteochondrosis).
When such symptoms appear for the first time, it is recommended to be examined by a neurologist.
The further development of the disease is manifested by obvious symptoms of discomfort:
Backache
Severe pain in the back (along the spine). The pain can radiate to the limbs.
Numbness of fingers
The typical manifestation of osteochondrosis is numbness of the fingers and toes.
Restrict sports activities
Even if the physical exertion is small, the pain will increase (for example, due to shaking and bumps during transportation). Pain leads to severe restrictions on mobility and sports activities.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
The main role of diagnosing osteochondrosis belongs to instrumental research: radiography, computed tomography, MRI.
It may be necessary to confirm that the observed symptoms are not caused by other medical conditions. For the purpose of differential diagnosis, general and biochemical blood tests, general urine tests, and ultrasound examinations of internal organs are performed.
Spine X-ray
Take X-rays of the problem areas of the spine. Which department needs to be checked is determined based on the patient’s chief complaint.
Computed tomography (CT)
Computed tomography (MSCT) can obtain more information pictures of the pathological process and determine its severity. In particular, MSCT makes it possible to detect intervertebral hernias.
Computed tomography is performed when X-ray data is insufficient.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
MRI is the most useful method for diagnosing osteochondrosis. In some cases (for example, if thoracic osteochondrosis is suspected), MRI cannot be exempted. Magnetic resonance imaging allows visualization of cartilage and soft tissues, based on which the root cause of the problem can be located as accurately as possible and the cause of the disease can be determined.
Osteochondrosis treatment methods
It is recommended to start treatment of osteochondrosis as soon as possible, because in most cases, the pathological changes of the spine are irreversible. Therefore, the main purpose of treatment is to eliminate pain and prevent the further development of the disease.
Usually, the treatment process is very complicated and requires a separate prescription according to the patient's condition. This clinic is used to treat osteochondrosis:
medical treatement
First, treatment aims to prevent (eliminate) the pain syndrome. Use anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants (medicine that relaxes muscles).
In addition, in the treatment of osteochondrosis, drugs that improve blood circulation, chondroprotective agents (drugs that restore cartilage tissue), vitamin D and calcium preparations are used.
massage
Osteochondrosis massage can relieve muscle tension, stimulate blood flow in the spine, and improve metabolic processes. This helps strengthen the vertebrae and intervertebral discs, suppress inflammation and reduce pain.
physiotherapy
For osteochondrosis, physiotherapy methods such as electrophoresis, sonic induction, UHF, and magnetic therapy are used.
Reflexology
Reflexology for osteochondrosis is used as an additional treatment. Acupuncture helps relieve pain, reduce inflammation, normalize blood circulation, and increase the effect of the medications used.
physiotherapy
Physical therapy of osteochondrosis is mainly aimed at eliminating pain and restoring the mobility of the spine. Use a set of specially selected exercises.
Prevent osteochondrosis
As a prevention of osteochondrosis, the clinic doctor recommends:
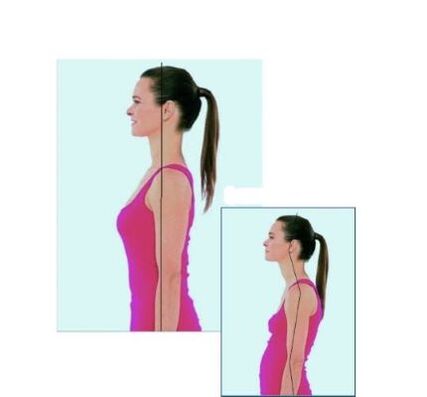
- Maintain the correct posture. The posture is the usual posture of the body when standing. Ideally, the head and back should be on the same vertical line, the shoulders should be on the same horizontal line, the abdomen should be tucked in, and the chest should be straight. Physical habits are developed through exercise. Therefore, posture must be monitored-do not bend over or become listless;
- Lead an active lifestyle and do gymnastics;
- Hanging on a horizontal bar is useful-when the spine is stretched;
- Sleep on a hard mattress. It is recommended to buy orthopedic mattresses and pillows;
- Follow a balanced diet and eat foods that contain enough vitamins and minerals.